KCNA
Kubernetes architecture
Simple definitions
Node: node is a worker machine where container run
Cluster: set of node
Master node: orchestrate the nodes
Components
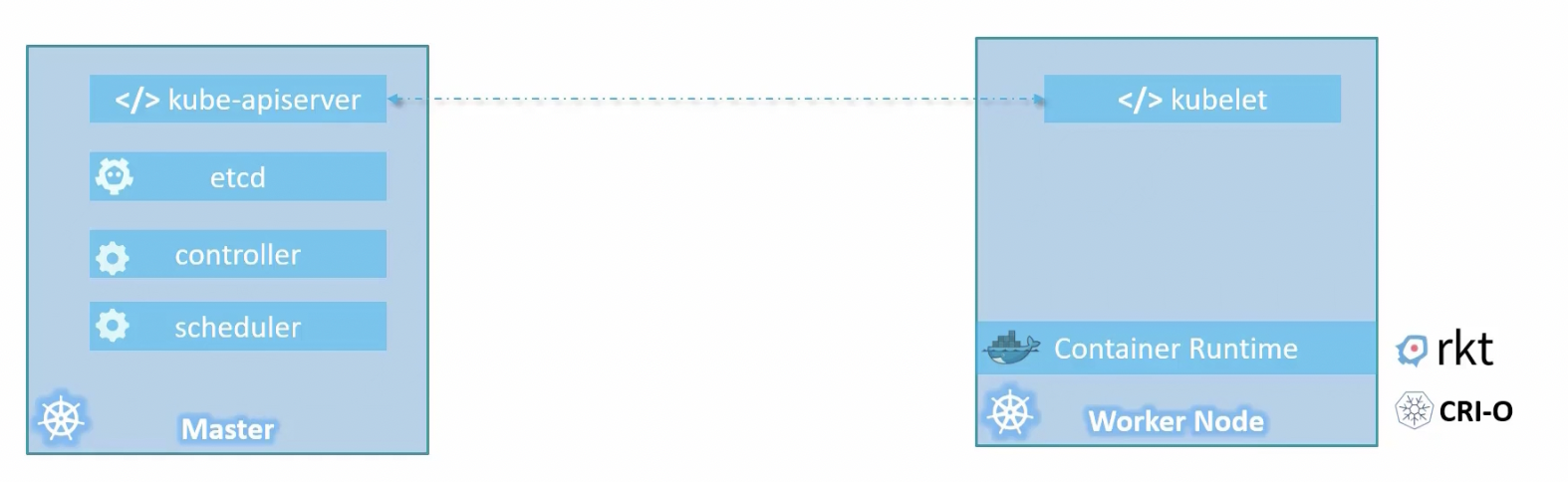
- Api server: frontend of the architecture. With api server you can talk with the cluster
- etcd: Distributed Hash Table **(**DHT) that contains all info of the cluster
- kubelet: agent that run in all node. Run stop container, interact with the kube api server of the master.
- container runtime: runtime where containers run
- controller: control the state of the cluster, restart pods if fails
- scheduler: distribute works on the nodes
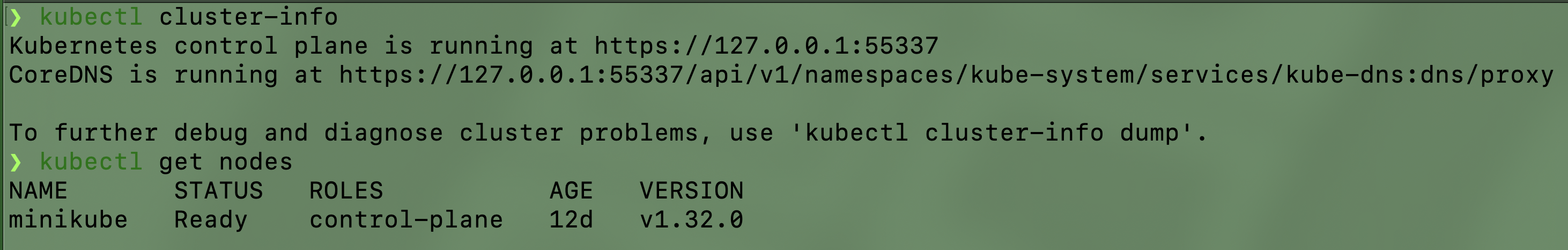
Kubectl
CLI command for talk with the cluster
- kubectl get nodes: get info about nodes
- kubectl cluster-info: get info about the cluster
Container runtime interface CRI
CRI: define an interface of grpc methods for support other container runtime
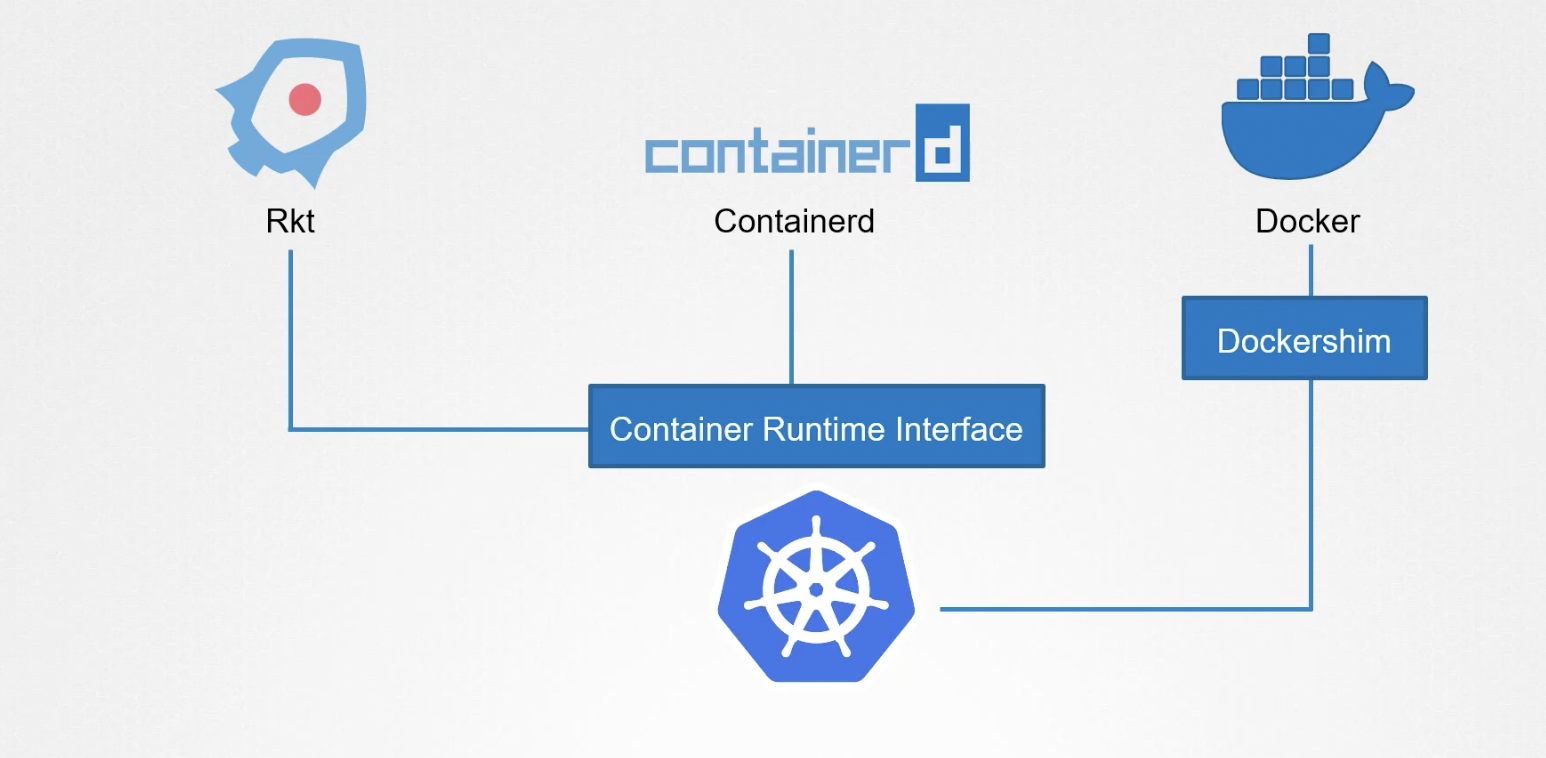
Dockershim is deprecate
Kubernetes basic resources
Pod
Pod: encapsulate containers, run in a node
Multi-Container pods: pods that run multi-container. (usually helper container for the main app). Containers share the same network and resources (run in the same virtual host)
Commands
Run command: run pods
kubectl run nginx --image=nginx
Get pods: return info about current pods in the cluster
kubectl get pods
kubectl get pods -o wide
Describe pod: give advance information about the pod
kubectl describe pod nginx
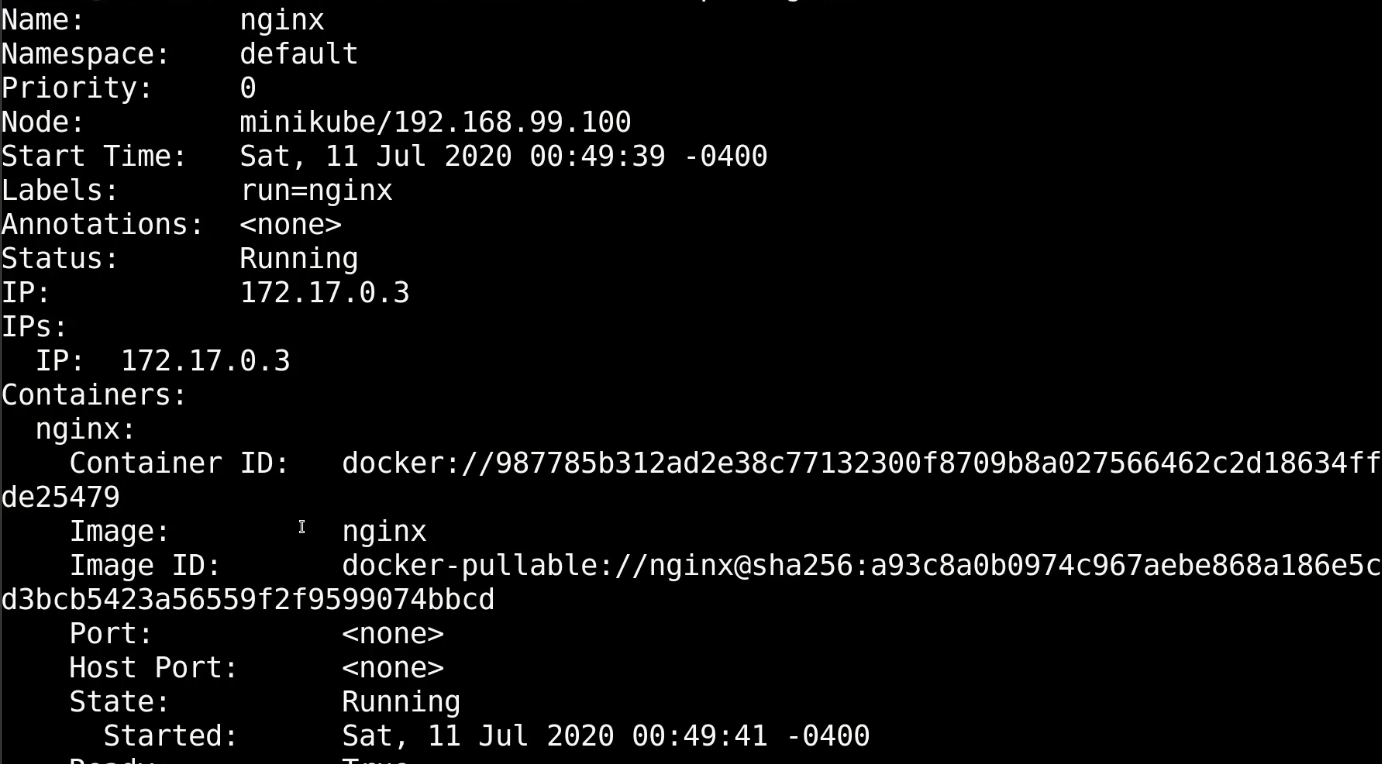
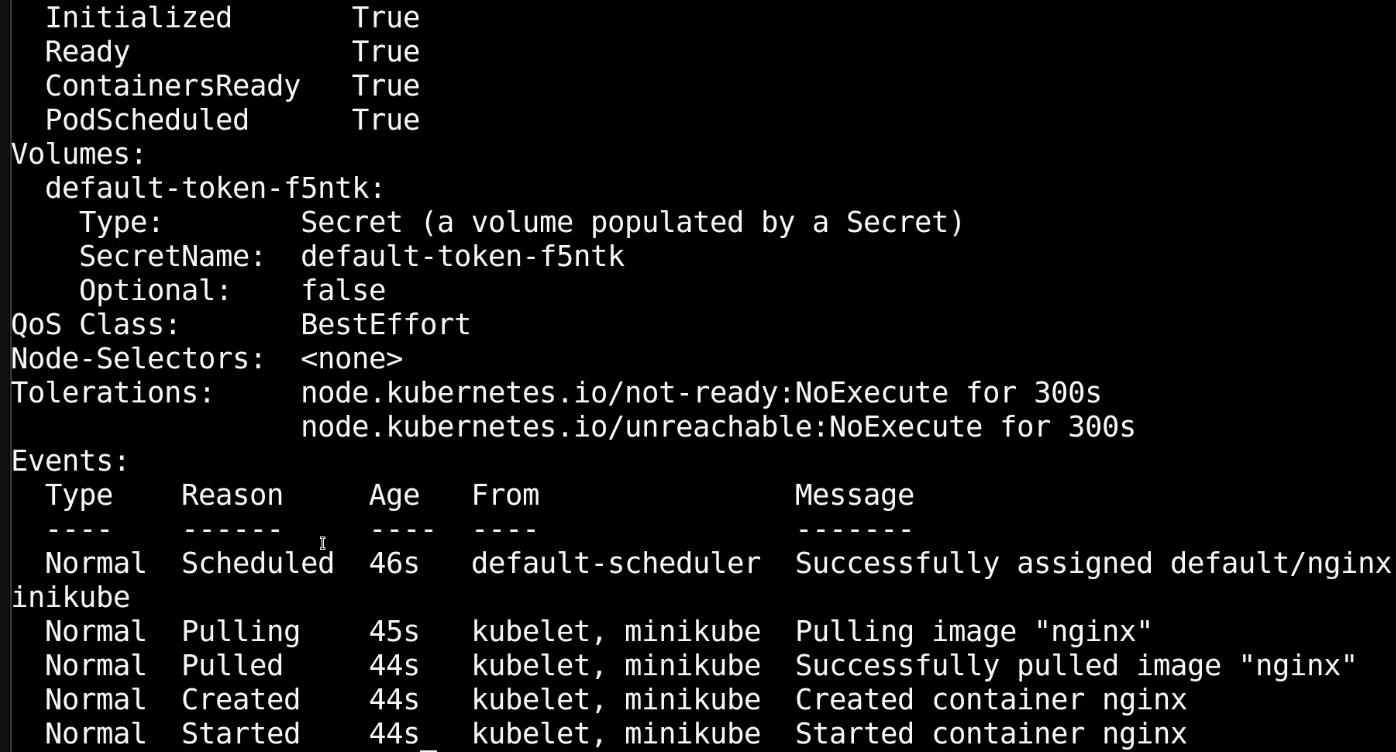
namespace, name, node where container run, container ip, volumes, events
Pod yaml definition
apiVersion: #api version of object
kind: #kind of object
metadata:
name: #pod-name
labels:
#dictionary-metada
#pippo: pluto
spec:
containers:
#List of container
- name: #container name
image: #image of container
| Kind | Version |
|---|---|
| Pod | v1 |
| Service | v1 |
| ReplicaSet | apps/v1 |
| Deployment | apps/v1 |
Replicaset
Replication Controller (Deprecated version fo replicaset): control the status of the replicaset, if one replica go down, automatically restart the replica. Spans accross multiple node

Replicaset: set of pods for HA, can manage pod created before of the replicaset
ReplicaSet Yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ReplicaSet
metadata:
name: my-app-replicaset
labels:
app: myapp
type: frontend
spec:
template:
metadata:
name: myapp-pod
labels:
app: myapp
type: frontend
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
replicas: 3
selector: #for managing pod created before the replicaset
matchLabels:
type: frontend # labels of the pod
ReplicationController Yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ReplicationController
metadata:
name: my-app-rc
labels:
#dictionary-metada
app: myapp
type: frontend
spec:
template:
# Here you set the template of the pod
metadata:
name: myapp-pod
labels:
app: myapp
type: frontend
spec:
containers:
#List of container
- name: nginx
image: nginx
replicas: 3 # specify the number of replica
Scale replicaset
- Update replicaset yaml number
- kubectl scale —replicas=6 -f replica.yaml
Deployments
Deployments: encapsulate replicaset.
Difference with replicaset: you can rollout rollback new version of the app
apiVersion: v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: my-app-deploy
labels:
app: myapp
type: frontend
spec:
template:
metadata:
name: myapp-pod
labels:
app: myapp
type: frontend
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
type: frontend
Rollout
Revision: version of one deployment
kubectl rollout status <deploymentname>
kubectl rollout history <deploymentname>
Recreate strategy: deployment strategy of recreate deployment
Rolling update: upgrade some set of pods per times
Rollback
Rollback: Return to the previous version of revision (previous replicaset)
kubectl rollout undo <deploymentname>
Apply Command
Apply Command: when you apply live object, last applied json configuration and local file are revisioned for making the changes
Live object configuration: mantain the status about the k8s object
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: annotation that olds last apply in json
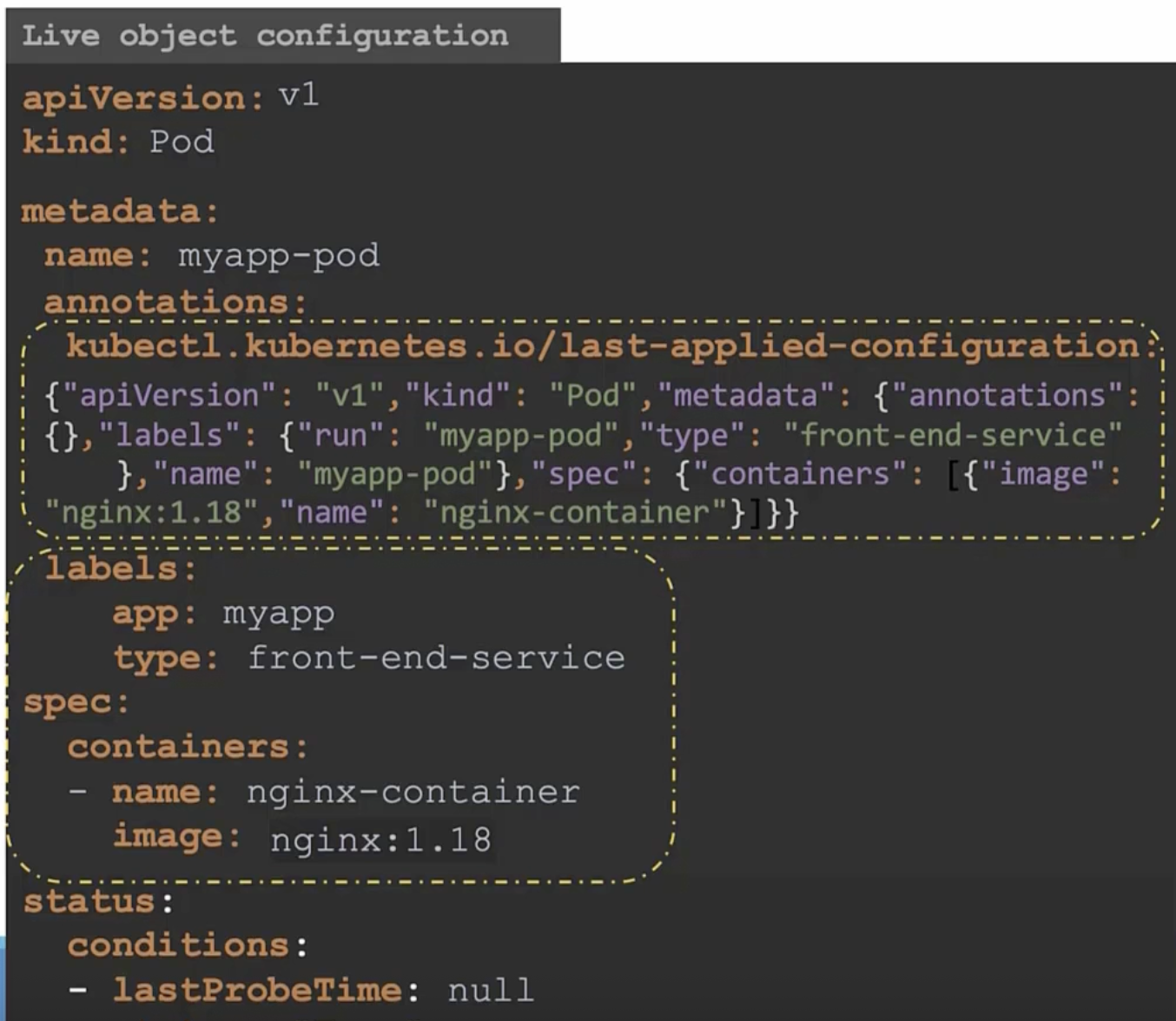
Namespace
Namespace: space that group resource
DNS: naming System of the namespace. identify resource in the namespace
- In the same namespace: entity name
- in other namespace: entityname.namespacename.svc.cluster.local
- entityname → name of the entity
- namespacename → name of namespace
- svc → service
- cluster.local → cluster domain

ResourceQuota: specify the limit of the namespace resource
Scheduling
Manual scheduling
With scheduler: scheduler automatically identify node where to schedule the pod
Without scheduler: use nodeName
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
name: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
nodeName: nodename
nodeName: identify in witch node pod is scheduled → only at creation time
Pod-bind-definition: can change the node where pod is scheduled after creation time
apiVersion: v1
kind: Binding
metadata:
name: nginx
target:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Node
name: nodename
Labels and selector and annotations
Selector: identify object with filtered labels
Labels: custom properties for identify objects
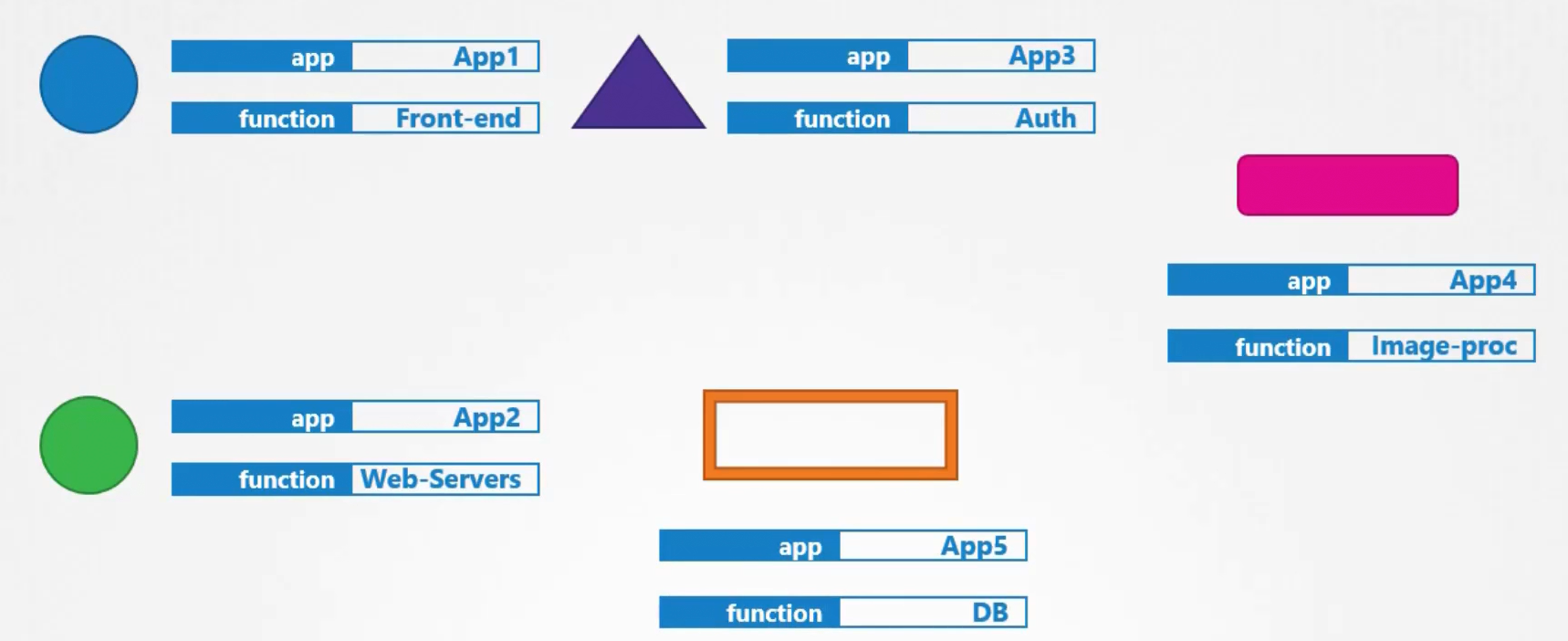
metadata:
labels:
app: App1
function: Front-end
selector:
matchLabels:
app: App1
Annotations: for additional information purpose
Tains and Tolerations
Taint and tolerations restrict which pods a node accepts
Tains: restrict which pod in which node
Tolerations: specify which pod can tolerate a tains (can be schedule in the node)
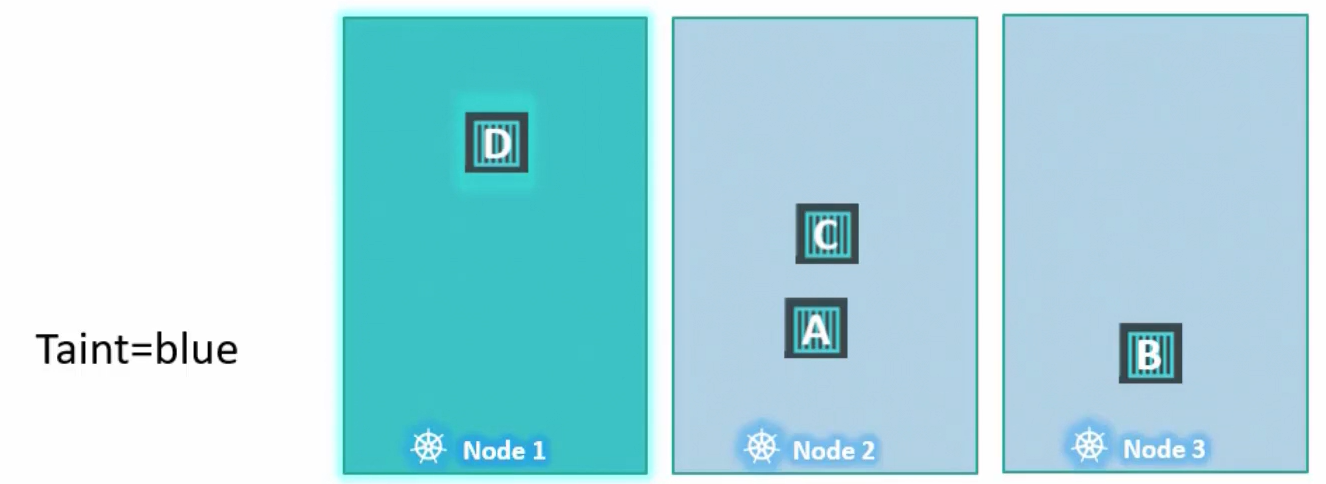
# Add taint to a node
kubectl taint nodes node-name key=value:taint-effect
Taint effect:
- NoSchedule: no place in the node
- PreferNoSchedule: avoid place in the node
- NoExecute: new pods are not scheduled in the node
# Add tolerations to a pod
spec:
tolerations:
- key: "app"
operator: "Equal"
value: "blue"
effect: "No Schedule"
Master node: blocked with a default taint
Node selector and Node affinity
Node selector: Schedule a pod in a labeled node (basic expression)
# label a node
kubectl label nodes <node-name> <label-key>=<label-value>
spec:
nodeSelector:
size: Large
Node affinity: ensure pod are in a particular node (advanced expression)
spec:
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
| DuringScheduling | DuringExecution | |
|---|---|---|
| Type1 | Required | Ignored |
| Type2 | Preferred | Ignored |
| Type3 | Required | Required |
| Type4 | Preferred | Required |
- DuringScheduling:
- require: require the node
- preferred: try to schedule in the prefferedNode
- DuringExecution (after first scheduling)
- reuquired: require preference
- ignored: ignore preference
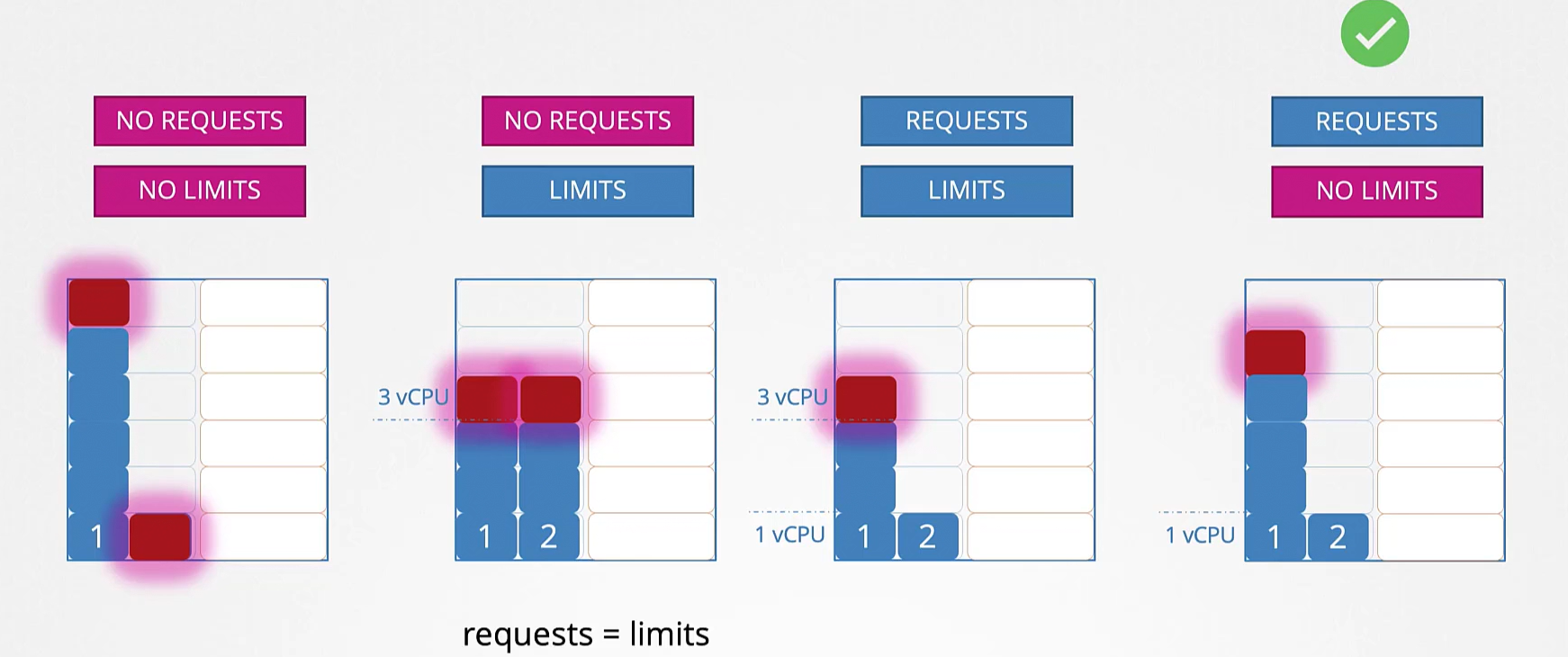
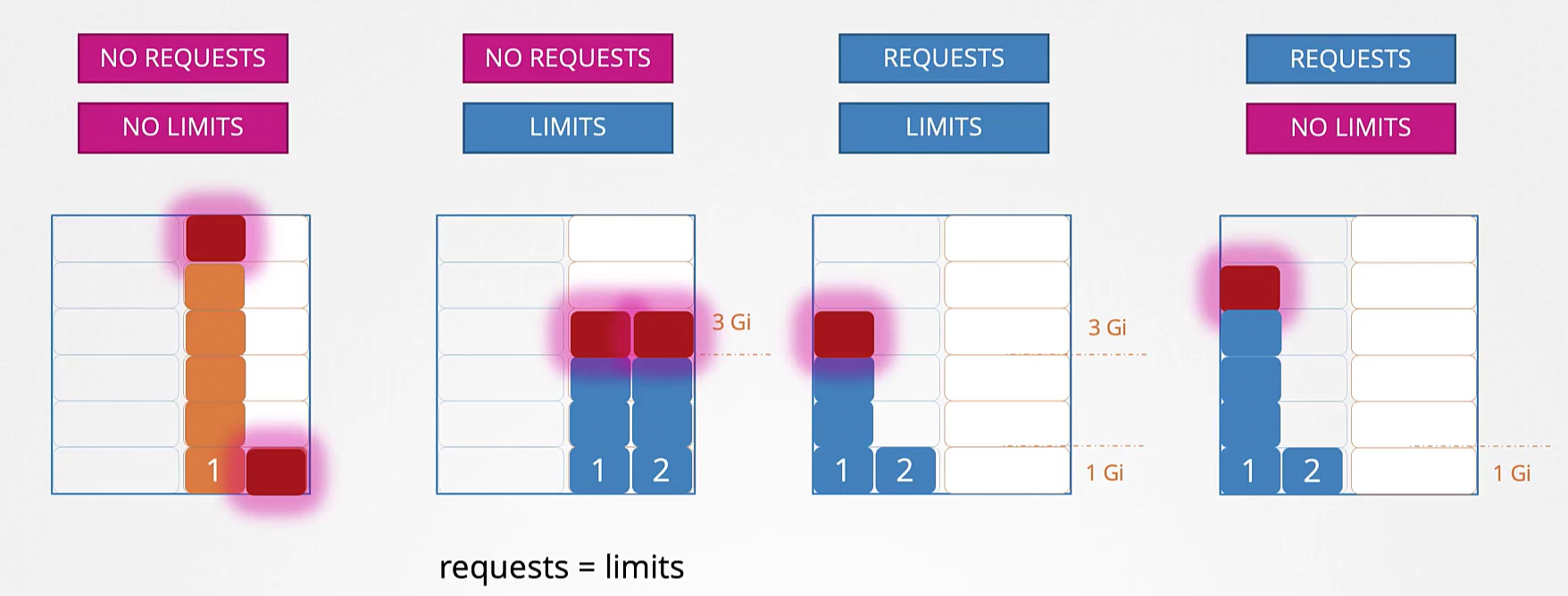
Resource limits
Resource request: container request some hardware resource, scheduler try to meet the request
Resource limits: limit the maximum resources a container can request
spec:
containers:
resources:
requests:
memory: "4Gi"
cpu: 2
limits:
memory: "8Gi"
cpu: 4
Exceed Limits:
- Cpu: throttle (slower) cpu
- Memory: terminated with OOM (out of memory) error
Default behaviour: container can use all resource of the node
LimitRanges: define default resource for container in a namespace
apiVersion: v1
kind: LimitRange
metadata:
name: cpu-resource-constraint
spec:
limits:
- default:
cpu: 500m
defaultRequest:
cpu: 500m
max:
cpu: "1"
min:
cpu: 100m
type: Container
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: LimitRange
metadata:
name: ram-resource-constraint
spec:
limits:
- default:
memory: 500m
defaultRequest:
memory: 500m
max:
memory: "1"
min:
memory: 100m
type: Container
Resource quota: limit in all worker node of the cluster
apiVersion: v1
kind: ResourceQuota
metadata:
name: resource-quota
spec:
hard:
requests.cpu: 4
requests.memory: 5Gi
limits.cpu: 10
limits.memory: 10Gi
DaemonSet
DaemonSet: run a copy of a pod in each node of the cluster (monitoring, logs collector)
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metada: #Daemon set metadata
name: monitoring-daemon
spec:
selector: # specify which pod do Daemnon
matchLabels: # daemonset pod with labels app == monitoring-agent
app: monitoring-agent
templtate: # defines the template of the pod to Daemon
metadata:
labels:
app: monitoring-agent
spec:
containers:
- name: monitoring-agent
image: monitoring-agent
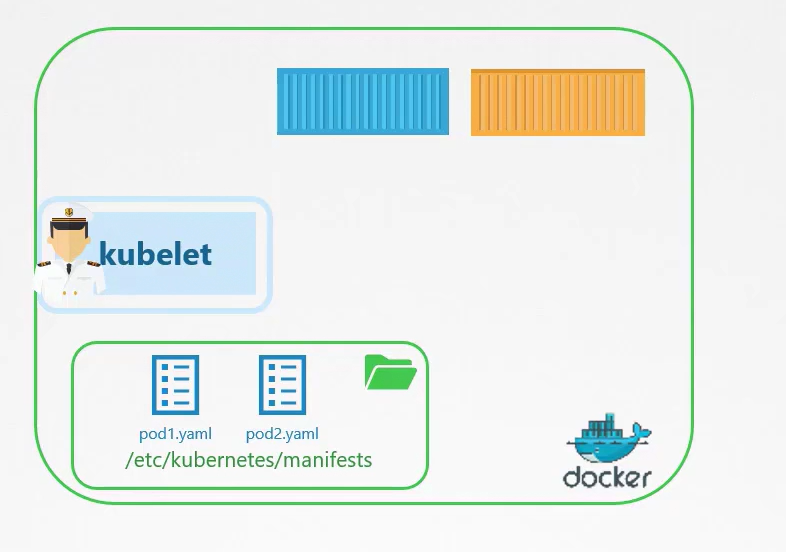
Static pod
Kubelet: can manage alone a node if the master is not online
Static pod: pods deployed by a kubelet in a signle node
- pod-manifest-path: path where yaml pod’s definitions files are stored in the
Use case: for create a new plugin in the master node
- Install kubelet in the node
- insert pod definitions yaml files of the core services in the stati file path
Multiple scheduler
kube-scheduler: default scheduler
custom-scheduler: user created
apiVersion: kubescheduler.config.k8s.io/v1
kind: KubeSchedulerConfiguration
profiles:
- schedulerName: my-scheduler
plugins:
Scheduling
Scheduling queue (PrioritySort plugin): queue of pods that wait to be scheduled (priority queue).
- PriorityClassName: property of pod (spec.priorityClassName).
- PriorityClass: create a priority class (high number high priority)
apiVersion: scheduling.k8s.io/v1 kind: PriorityClass metadata: name: my-priority value: 100000000 globalDefault: false description: "My priority"Filter phase (NodeResourcesFit, NodeName, NodeUnschedulable plugins): filter possible node for the pod
Scoring (NodeResourceFit, ImageLocality plugins): score the filtered node, high score ⇒ choose
Binding (DefaultBinder plugin): pod bind to a node
Cluster Security
Security basics
Host connection security:
- Root access disable
- Password authentication disabled
- Ssh based
Authentication to kube-apiserver:
- Token
- Username password
- ceritifcates
- Service accounts
- LDAP
Authorization to the kube-apiserver:
- RBAC
- ABAC
- Node Author
- Webhook Mode
Connection to kube apiserver:
- Secured by TLS
Network policy:
- Restrict access from pod in one node to pod in another node
Authentication
Account:
- User: person
- Service Accounts: process, services
Auth mechanism:
- Static username-password file: password, username, userid in csv file
- Static token file: token, user, group in csv file
- TLS Certificate: ca that emit certificate
Kubeconfig
Kubeconfig: File for easy configuration of k8s kube-api-server call
- Clusters: info about the cluster
- Contexts: which user for which cluster
- Users: users
apiVersion: v1
clusters:
- cluster:
certificate-authority-data: base64certificate
server: serverip
name: nome
contexts:
- context:
cluster: nome
user: kubernetes-admin
name: kuebrnetes-admin@kubernetes
users:
- name: kubernetes-admin
user:
client-certificate-data: base64certificate
client-key-data: base64certificate
# list $HOME/.kube/config configuration
kubectl config view
# set current context
kubectl config use-context <context-name>
Api groups
Example of kube-apiserver call:
curl https://kube-api-server-ip:6443/api/v1/pods
Api group:
- “/version” :
- “/api” : core group
- “/v1/pods”
- “/v1/namespaces”
- “/v1/services”
- “/v1/secrets”
- “/v1/configmaps”
- “/v1/nodes”
- “/apis”:
- “/apps/v1/deployments”
- “/apps/v1/replicasets”
- “/apps/v1/statefulsets”
- “/metrics”
- “/logs”
# list all api group
curl http://kube-api-server-ip:6443 -k --key mykey.key --cert mycert.cert --cacert ca.crt
# list all api of apis group
curl http://kube-api-server-ip:6443/apis -k --key mykey.key --cert mycert.cert --cacert ca.crt
kubectl proxy: proxy the kueb api server locally
curl http://kube-api-server-ip:8001-k
curl http://kube-api-server-ip:8001-k
WARNING: kubectl ≠ kube proxy
Authorization
Node base: Node authorizer
Role base: group user in one role. associate permission to the role
Attribute base: associate permission to an user. with a policy file
Webhook: thirth party agent permit access
Role based
Role are namespaced
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: developer
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["list", "get", "create", "update", "delete"]
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: developer-devuser-binding
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: developer
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
subjects:
- kind: User
name: dev-user
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
# check if my user have permission
kubectl auth can-i create deployments
kubectl auth can-i create deployments --as dev-user
Cluster role
Cluster role: is cluster scoped
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: cluster-admin
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["list", "get", "create", "update", "delete"]
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: cluster-admin-adminuser-binding
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
subjects:
- kind: User
name: cluster-admin-user
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
Service account
Service account: user for application, scripts, role, agents, non-human entities
# create sa
kubectl create serviceaccount nome
Service account token: jwt token associated with the sa
kuebctl create token sa-name
Pods creation: in auto k8s provide default sa
directory “/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount”: directory mounted inside the pod. it contains sa tokens
spec:
serviceAccountName: test-sa
spec:
automountServiceAccountToken: false
Image security
kubectl create secret docker-registry secret-contains-docker-regostry-info \
-- docker-server = \
-- docker-username= \
-- docker-password= \
-- docker-email= \
spec:
containers:
- name: test
image: privateregistry/image
imagePullSecrets:
- name: secret-contains-docker-regostry-info
Network policies
Default ingress/egress policy: all pods allow rules traffic for ingrees/egress

Network policy: allow/deny traffic in ingress/egress in a pod
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: access-nginx
spec:
podSelector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
ingress:
- from:
- podSelector:
matchLabels:
access: "true"
Networking
Cluster networking
Node. each node has at least 1 ip from the network and 1 network interface and 1 unique mac address and 1 hostname
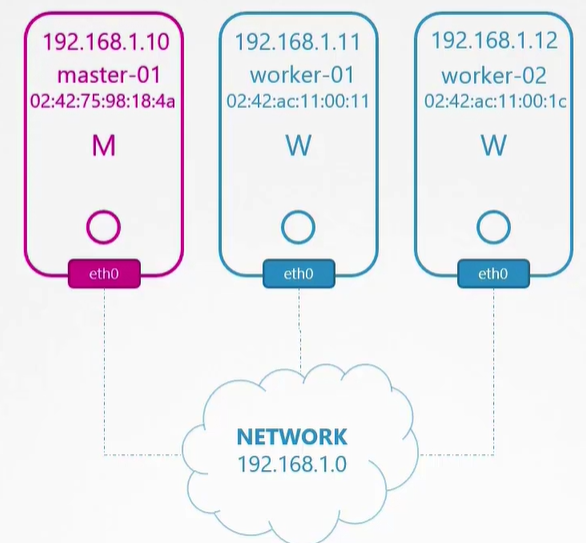
Common ports on master node:
- 6443: kube-api server
- 2379: etcd
- 10250: kubelet
- 10259: kube-scheduler
- 10257: kube-controller-manager
Pod newtorking
Pod network model:
- every pod 1 ip
- every pod in the same node should comunicate
- every pod in the same node should comunicate without nat
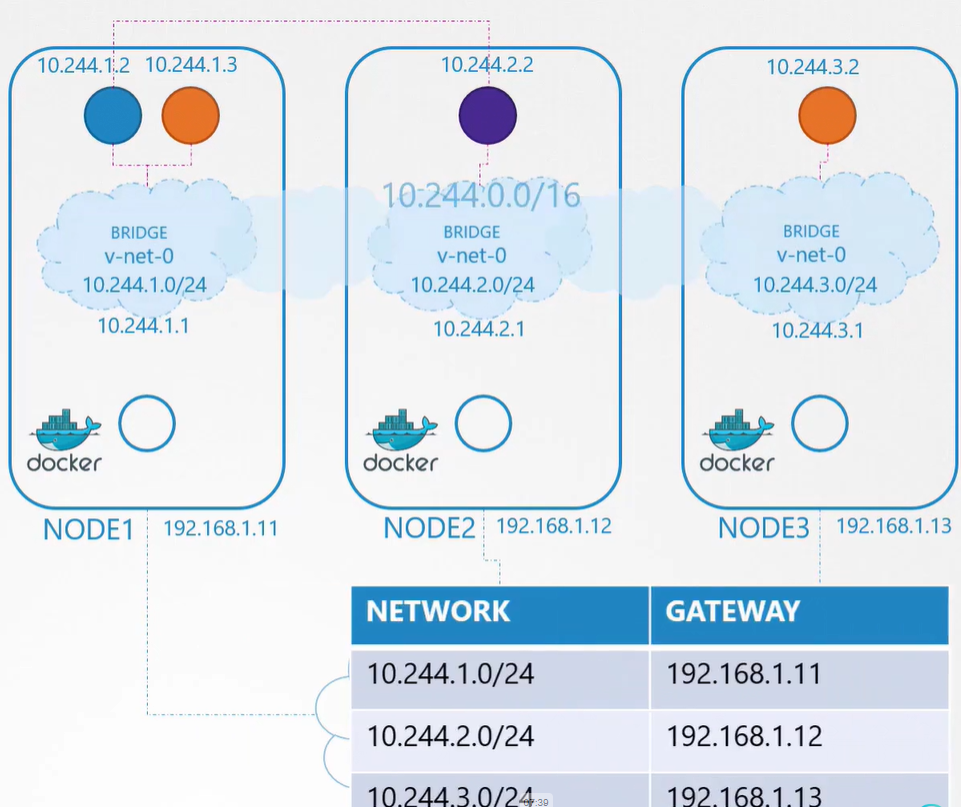
All the node are part of a common network connect through a router.
Each node has a intranode network for give ip to pods
Pods of differente nodes comunicate through the router
Container network interface CNI
Container network interface: define standard networking for pod
DNS
Core-Dns: dns server in the cluster
Pod registration is not enable by default
| Hostname (name of pod) | Namespace | Type | Root cluster domain | IP Address |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| web-service | apps | svc | cluster.local | 10.107.37.188 |
| 10-244-1-5 | default | pod | cluster.local | 10.244.2.5 |
Resolving pod:
- in the same namespace:
- using hostname. es curl http://podname
- In different namespace:
- using hostname.namespace. es curl http://podname.namespacename
Resolving services:
Services type
Service: expose pod to the network
Service type:
- ClusterIP: expose service into the cluster network
- NodePort: expose service throught the static node ip
- LoadBalancer: expose a service throught external load balancer
- ExternalName: expose a service throught a cname in the dns
Ingress
Ingress: Layer 7 load balancer into k8s cluster
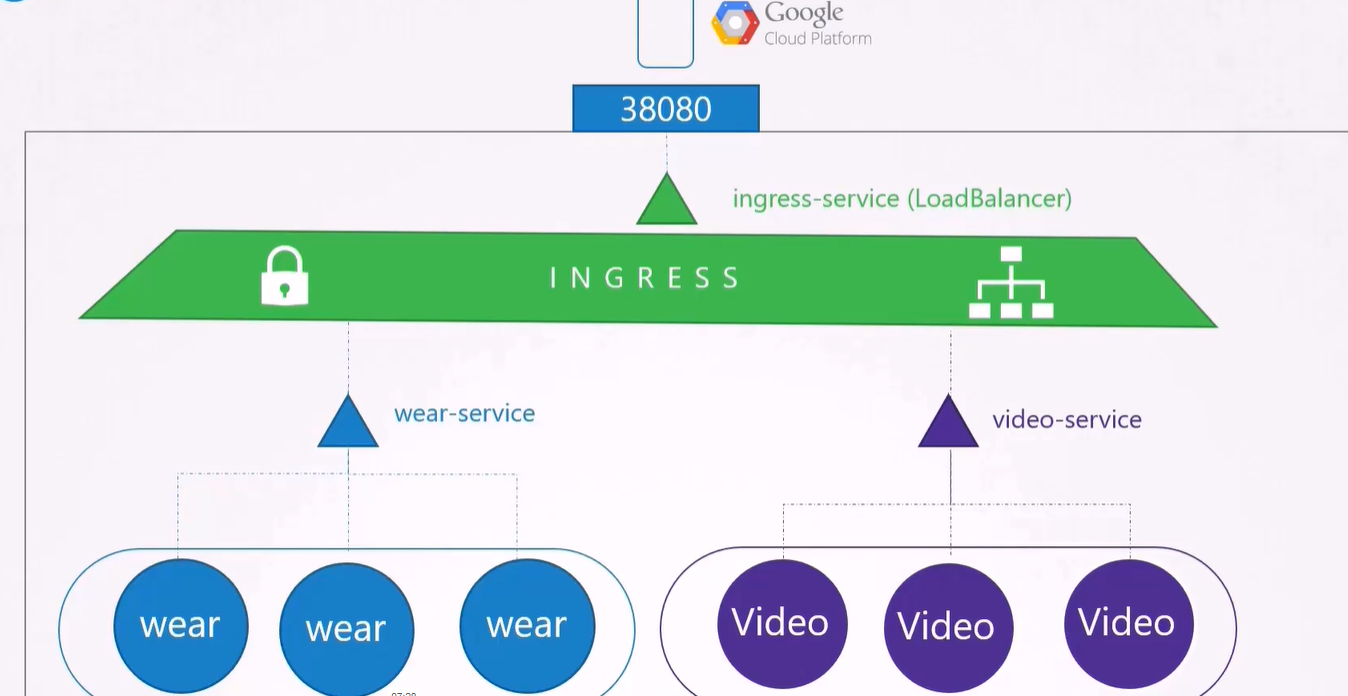
Expose ingress: througth nodeport or load balancer
Ingress controller: controll ingress
- Istio
- nginx
- gcp load balancer
Ingress resources: resource controlled by controller
Ingress rule: routing rules
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: minimal-ingress
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx-example
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /testpath
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: test
port:
number: 80
Service mesh
Sidecar
Sidecar: helper container in the same pod of the main container
Envoy
Envoy: open source proxy. Can be used as Sidecar container in the pod for manage authorization and other stuff
Service mesh
Service mesh: architectural layer for manage traffic between microservices
Architecture:
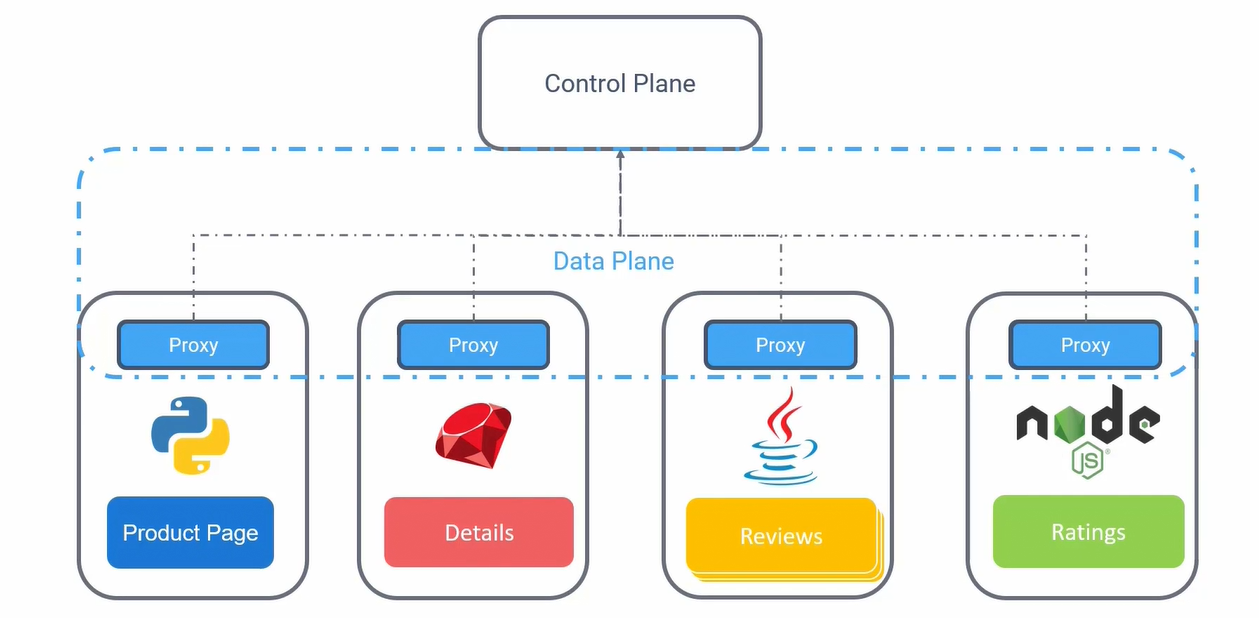
- Sidecar proxy container: each pod has a sidecar proxy container for manage logging, authorization, authentication, monitoring, traffic
- Control plane: manage data plane
- Data plane: architectural layer for comunication between proxy
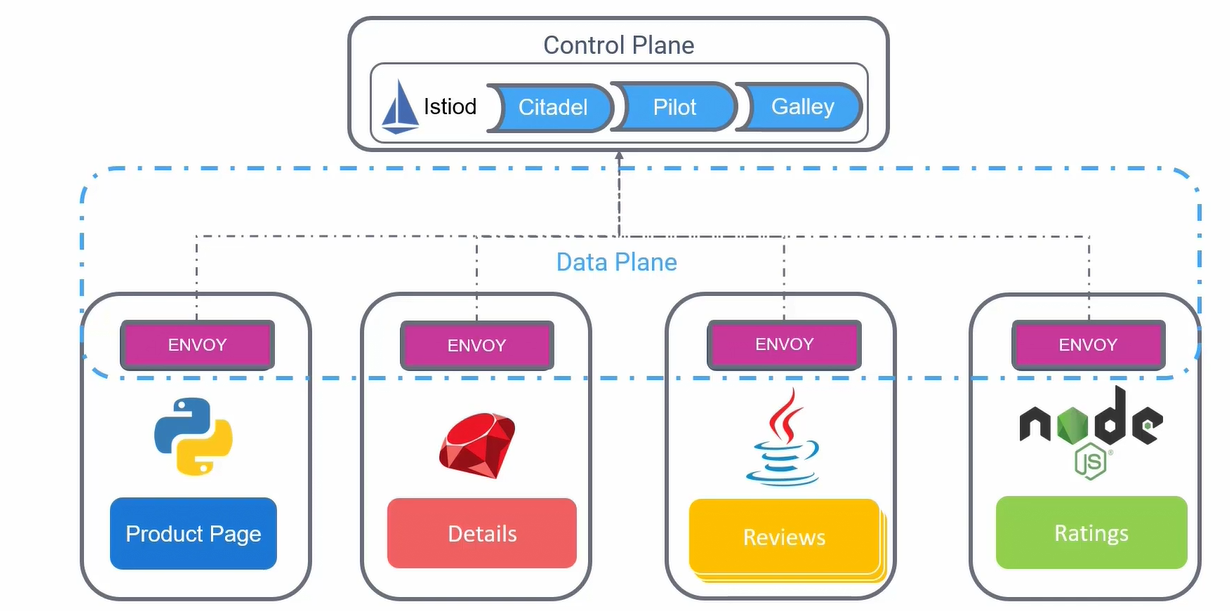
Istio
Istio: open source service mesh
Citadel: manage ssl certificate
Pilot: service discovery
Galley: invalidate configuration
Istiod: main daemon that contains citadel, pilot, galley
Istioagent: pass secrets to envoy proxy
Storage
Storage in docker
- “/var/lib/docker” docker data fs
Image layers: layer created when you build the image, one for instruction. docker cache every layer for future update
Container layer: layer created when the container is up. go down when container is destroy
Volumes: persistent volume mounted in “/var/lib/docker/volumes/
Container storage interface
Container strage interface (csi): standarize storage solution for k8s
Volumes
Volumes: ephimeral volume attached to pod
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metada:
name: random-number
spec:
containers:
- image: alpine
name: alpine
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c"]
args: ["shuf -i 0-100 -n >> /opt/number.out;"]
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /opt
name: data-volume
volumes:
- name: data-volume
hostPath:
path: /data
type: Directory
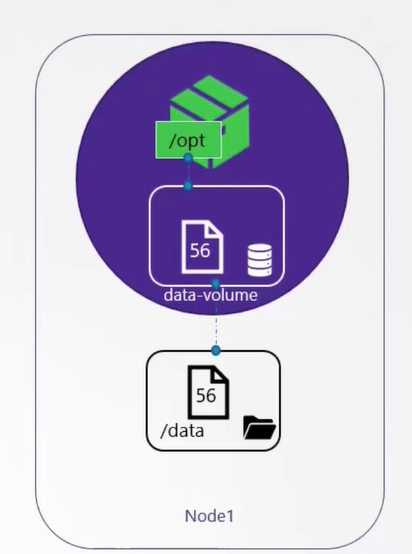
WARNING: the volume directory is different for every node. Use NFS, EFS, EBS, or other solutions for replication.
Persistent volume
PersisentVolume: persistent share volume, pod can claim some space
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: pv-vol
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce ## ReadOnlyMany ReadWriteOnce ReadWriteMany
capacity:
storage: 1Gi
hostPath:
## Supported storage solutions
PersistentVolumeClaim
PersistentVoluemClaim: claim storage from pod
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: myclaim
spec:
accessModes:
## access Mode
resources:
request:
storage: ## requested storage
spec:
volumes:
- name: data-volume
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: myclaim
Storage Classes
StorageClasses: dynamic provisione cloud storage, or storage solution like volume
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: google-storage
provisioner: kuebrnets.io/gce-pd
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: myclaim
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
storageClassName: google-storage
resources:
requests:
storage: 500Mi
---
spec:
volumes:
- name: data.volune
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: myclaim
Cloud native architecture
Horizontal Pod autoscaler
HPA: controller that automatically horizontal scale pod
Metric server: analyzed by horizontal autoscaler controller for autoscale pod deployment
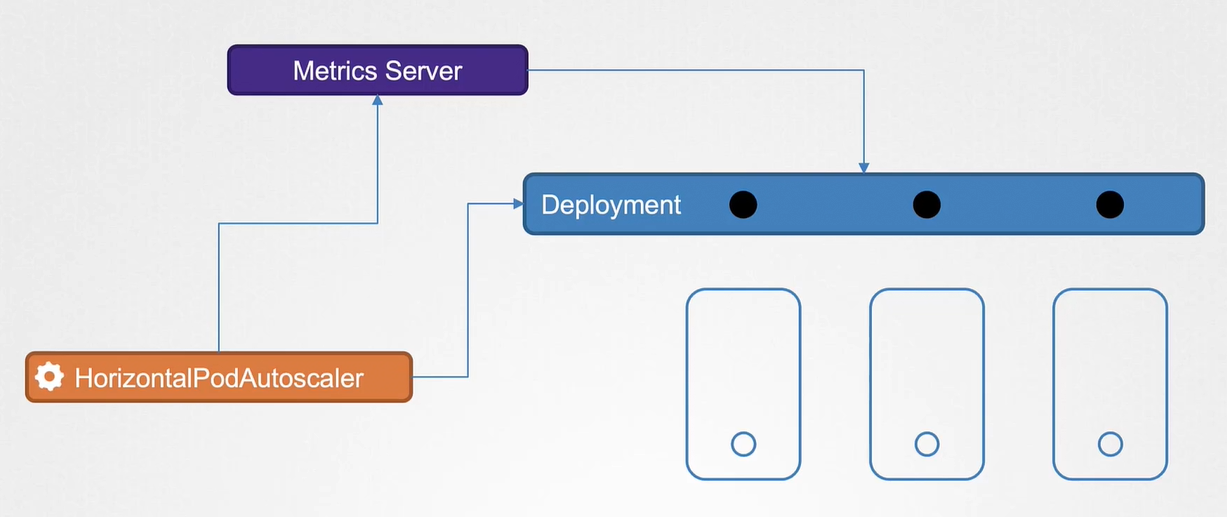
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2beta2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: myapp-hpa
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: nameofdeployment
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
- type: Resource
resouece:
name: cpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 50
Vertical Pod Autoscaler
VPA: controller that autoscale vertical a pod based the metric service metric
VPA Recommendation: part of the VPA that recommended potential resource request by pod
VPA Updater: updated the pod for meet VPA recommendation
VPA Admission controller: allign new pod creation with current reccomender request
Cluster Autoscaler
Cluster autoscaler: autoscale cluster node
Observability
Terms
Logs: text file with information about events of the system
Trace: identify a request in the system by one id, it is compose by spans
Spans: individual event of a trace
Metrics: identify the state of a system through numerical values
Prometheus: collect metrics
SLI/SLO/SLA
SLI: metrics about one aspect of a service
SLO: range or target of an SLI
SLA: contract that guaranties the SLO
Prometheus
Prometheus: open source framework for collecting metrics. can query metrics via prometheusSQL
Type of data: numeric metrics
Prometheus Architecture
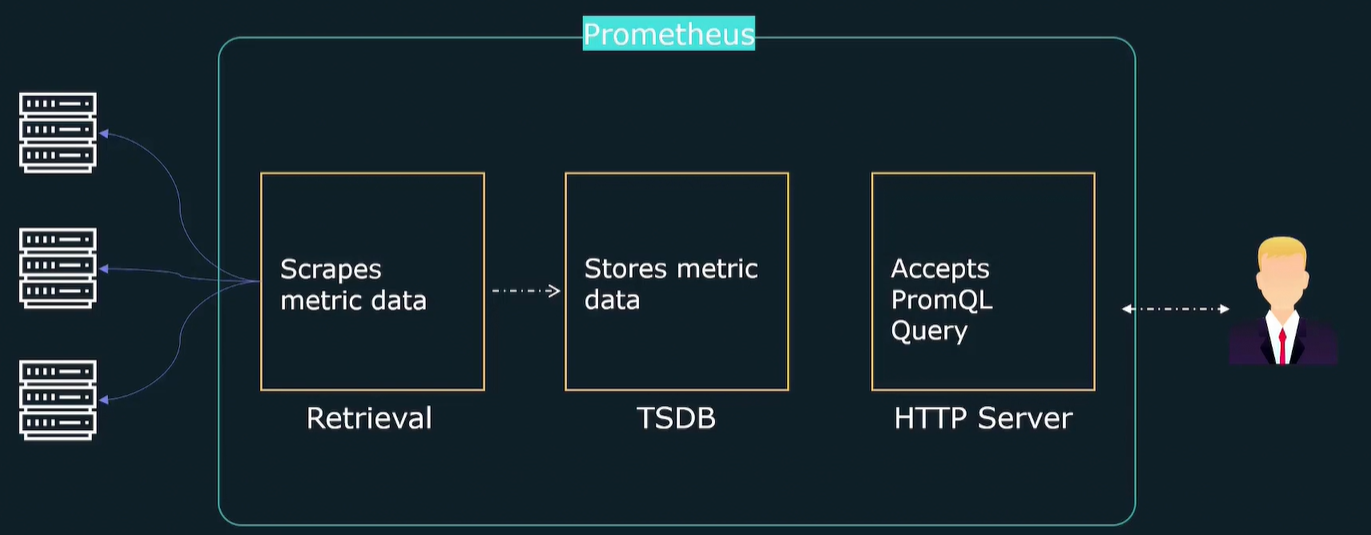
Retrieval: agent that retrieve datas from http servers
TSDB: internal database for storing data
HTTP Server: for prompting data from dB with PromQL
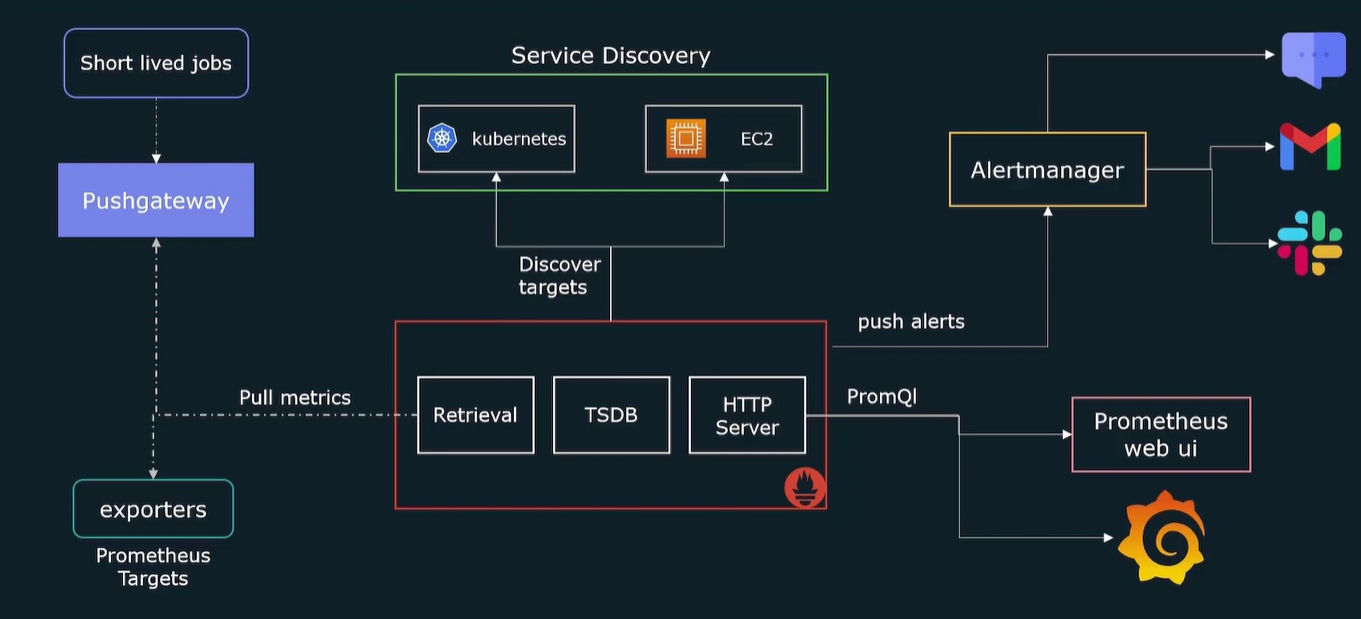
Exporters: interface for exporting metrics of a target
Pushgateway: gateway for exporting data from short live or ephemeral jobs
Service discovery: list of prometheus targets
Alert manager: alert at metrics
“/metrics” : path queried by prometheus for taking metrics
Pull based model: prometheus pull metrics not viceversa
Node Exporter
Node exporter: open source exporter for linux machines
Metrics structure
<metric_name>[<label1=value1>,<label2=value2>]<metric_value>
Docker observability
Docker engine metrics: metrics about docker engine
cAdvisor metrics: metrics about containers
K8s Observability
- Install node exporter in every node → daemnon set
- Install prometheus in the cluster → helm chart
- Install kube-state-metrics
Application Delivery
GitOps
GitOps: change infrastructure by accepted merge request on a repository
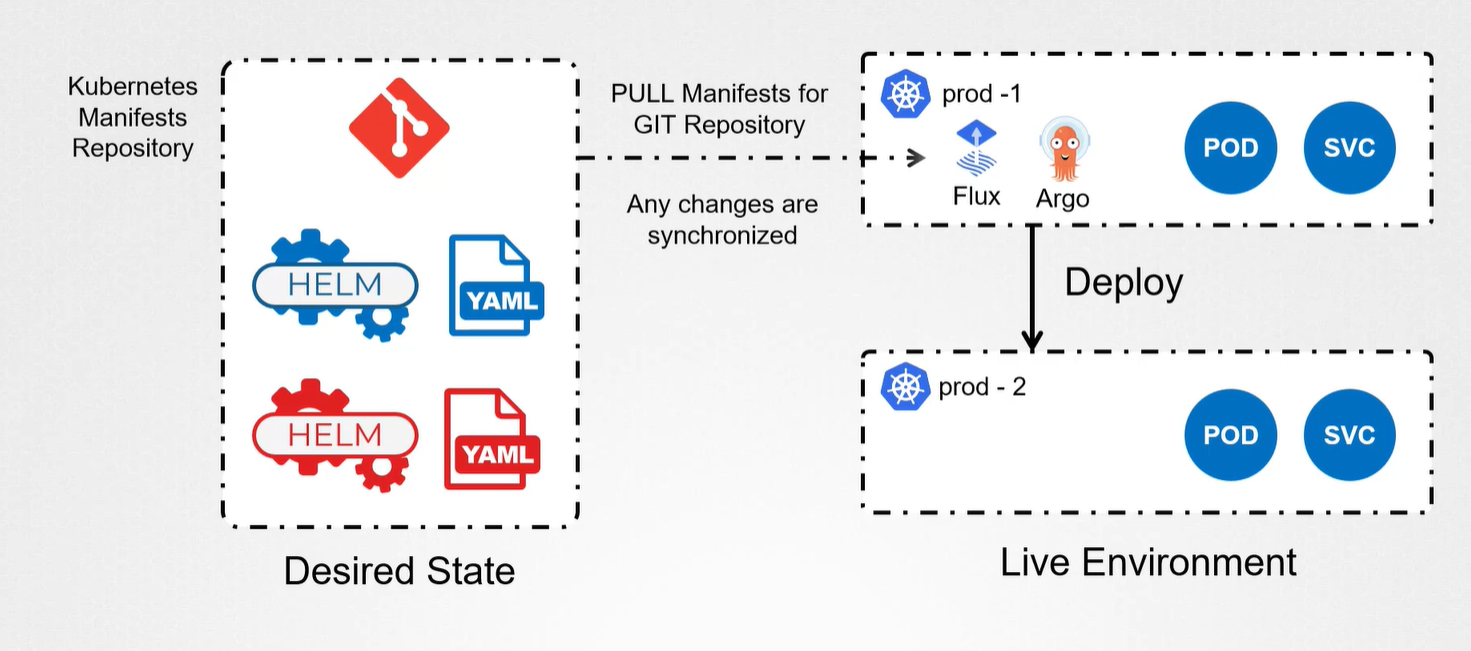
Flux: sync k8s app with the state on a git repository
ArgoCd: like flux but can monitor multiple repository
Jenkins X: cover entire CICD
Gitops Principle
Declarative: k8s state is declarade in yaml file stored in git
Versioning: each git state corrispond to a version
Pull model: agent pull and sync with merge request on git repo
Cycle: cycle process